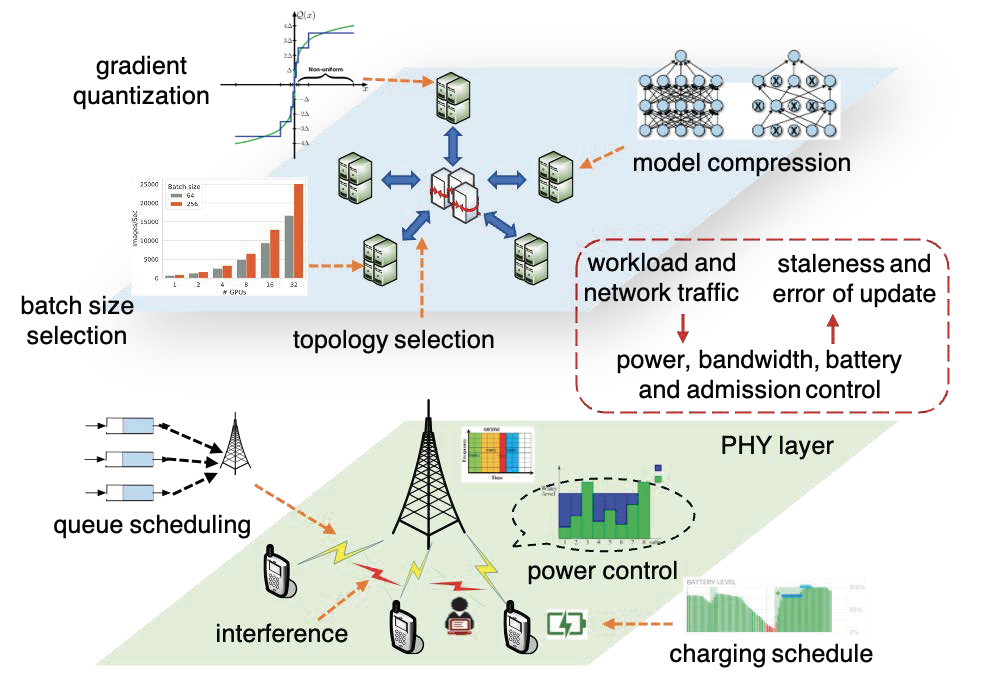
Today, given the growing sensing and computing power of smart devices, amplified by increasing concerns on data privacy, it is expected that a sizeable amount of AI/ML tasks will be collaboratively run at the devices in wireless networks, e.g., in federated learning. In this context, my research efforts are centered on two fundamental issues of distributed (reinforcement) learning algorithms: scalability and trustworthiness. Scalability is not only about computational efficiency, but also about communication overhead of running learning algorithms at the network edge; and robustness is concerned with changing system dynamics, varying network topologies, data leakage and adversarial attacks.
Federated learning at the network edge
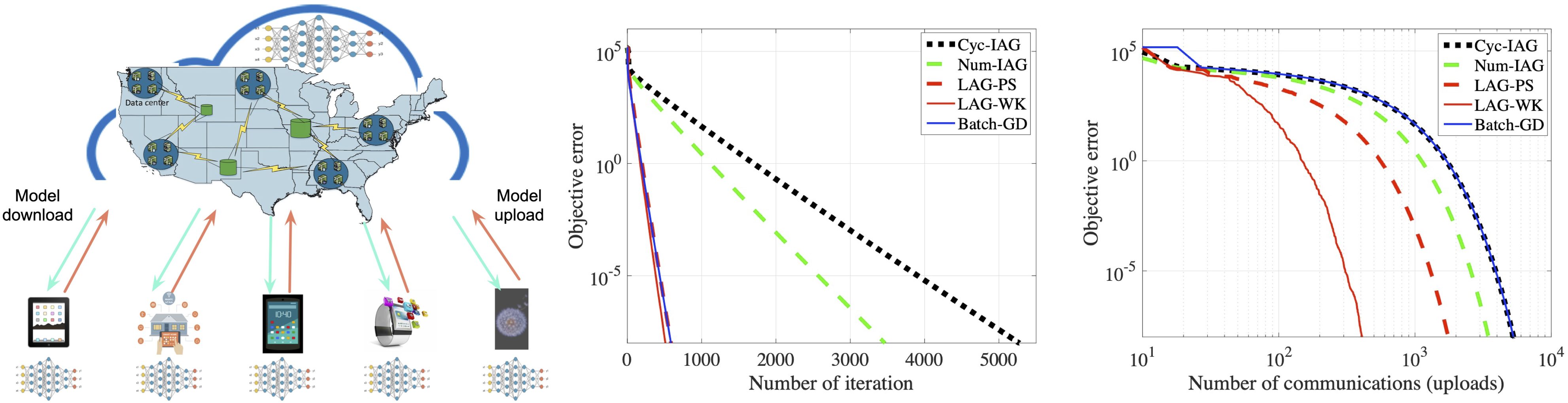
Conventional machine learning approaches require centralizing users’ data in a remote data center, which is known as cloud computing. In cloud computing, users’ data from the devices, such as smartphones, are transferred to the data centers which execute learning algorithms on CPU and GPU clusters. Considering the massive amount of devices, centralized learning using cloud computing becomes computationally intractable, and rises serious privacy concerns. To date, the widespread consensus is that besides data centers, future machine learning tasks have to be performed starting from the network edge, namely mobile devices. This is the overarching goal of federated learning. Towards this goal, my research efforts are centered on i) reducing the communication overhead during the learning processes; ii) improving the trustworthiness by developing attack and defense strategies; and, iii) developing new models for federated learning settings with imcomplete features. Our methods (LAG-WK and LAG-PS) with adaptive communication mechanism have been selected as the spotlight presentation in NeurIPS, which establish a provably reduced communication complexity in distributed learning. Our work on a new model for federated learning was recognized as the Best Student Paper Award of NeurIPS-Spicy workshop on federated learning.
 |
Related publications:
- T. Chen, G. B. Giannakis, T. Sun and W. Yin, ‘‘LAG: Lazily Aggregated Gradient for Communication-Efficient Distributed Learning,’’ Proc. of Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Montreal, Canada, December 3-8, 2018. (Spotlight talk and poster)
- J. Sun, T. Chen, G. B. Giannakis, and Z. Yang, ‘‘Communication-Efficient Distributed Learning via Lazily Aggregated Quantized Gradients,’’ Proc. of Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, Canada, December 3-8, 2019.
- L. Li, W. Xu, T. Chen, G. B. Giannakis, and Q. Ling, ‘‘RSA: Byzantine-Robust Stochastic Aggregation Methods for Distributed Learning from Heterogeneous Datasets,’’ Proc. of the Assoc. for the Advanc. of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Honolulu, Hawai, January 27-February 1, 2019. (Oral presentation)
- X. Jin, P.-Y. Chen, C.-Y. Hsu, C.-M. Yu, and T. Chen, ‘‘Catastrophic Data Leakage in Vertical Federated Learning,’’ Proc. of Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Virtual, December 6-14, 2021.
Distributed reinforcement learning over networked agents
From learning to control, reinforcement learning (RL) will play a critical role in many complex IoT tasks. Popular RL algorithms are originally developed for the single-agent tasks, but a number of IoT tasks such as autonomous vehicles, coordination of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), involve multiple agents operating in a distributed fashion. Today, a group of coordinated UAVs can perform traffic control, food delivery, rescue and search tasks. In this context, my research efforts in this direction are centered on studying the convergence rates, sample complexity, communication complexity and robustness of popular distributed and multi-agent RL (MARL) algorithms and characterizing their scaling effect as the number of distributed nodes increases.
Related publication:
- T. Chen, K. Zhang, G. B. Giannakis, and T. Başar, ‘‘Communication-efficient policy gradient methods for distributed reinforcement learning,’’IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems (TCNS), December 2020.
- S. Lu, K. Zhang, T. Chen, T. Başar, and L. Horesh, ‘‘Decentralized policy gradient descent ascent for safe multi-agent reinforcement learning,’’Proc. of the Assoc. for the Advanc. of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), virtual, February 2-9, 2021.
- Z. Wu, H. Shen, T. Chen, and Q. Ling, , ‘‘Byzantine-Resilient Decentralized TD Learning with Linear Function Approximation.,’’IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP), vol. 69, pp. 3839 - 3853, June 2021.