Optimally allocating limited computing and communication resources is a crucial task in resource-limited IoT environments. In this context, I have provided affirmative answers to the following intermediate questions:
i) Can we learn from historical data to improve the existing resource management schemes?
ii) Can we develop resource management schemes when the underlying models are not known?
The key novelty here is innovative statistical and interactive learning tailored for resource management tasks in IoT. Results in this direction have been disseminated as part of a tutorial we co-presented at GLOBECOM 2018, and summarized in our overview paper.
Statistical learning viewpoint of resource management
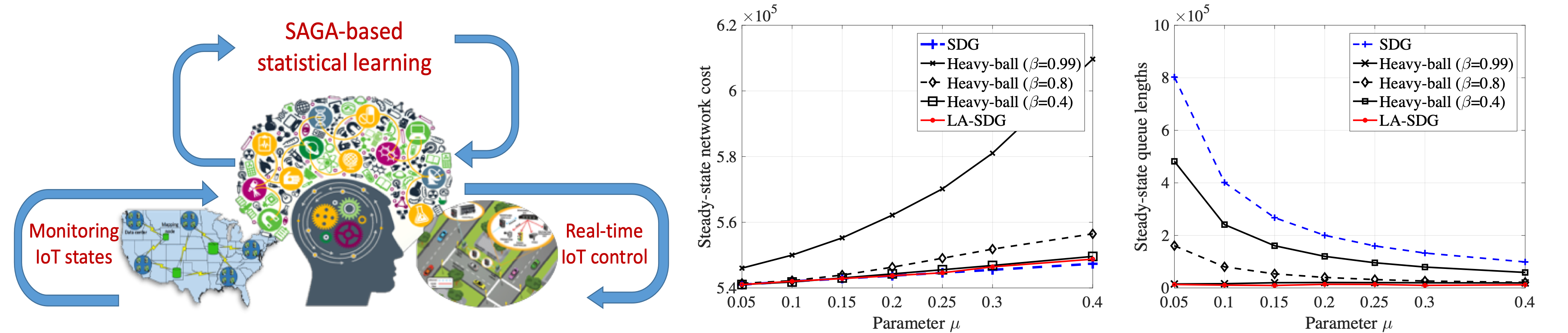
To date, most resource management schemes for IoT are based on a pure optimization viewpoint e.g., the dual (sub)gradient method (SDG), which incur large queueing delays and slow convergence. From the vantage point of IoT, our fresh idea is to leverage the abundant historical data collected by devices, and formulate the resource management problem as an empirical risk minimization (ERM) — a central topic of statistical machine learning research. In this context, we have developed a fast convergent algorithm. By cross-fertilizing advances of learning theory, we have also established the sample complexity of learning a near-optimal resource management policy. To boost performance in dynamic settings, we further introduced a learn-and-adapt resource management framework (LA-SDG), which capitalizes on the following features: (f1) it learns from historical data using advanced statistical learning tools; and, (f2) it efficiently adapts to IoT dynamics, and thus enables operational flexibility. Our proposed algorithms have been published in top signal processing and network optimization journals, where we have analytically shown that this novel algorithmic design can provably improve the emerging performance tradeoff by an order of magnitude. To demonstrate the impact of this work, we have applied it to mobile computing and smart grid tasks.
 |
Relevent publications:
- T. Chen, A. Mokhtari, X. Wang, A. Ribeiro and G. B. Giannakis, ‘‘Stochastic Averaging for Constrained Optimization with Application to Online Resource Allocation,’’ IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 65, no. 12, pp. 3078-3093, Jun. 2017.
- T. Chen, Q. Ling and G. B. Giannakis, ‘‘Learn-and-Adapt Stochastic Dual Gradients for Network Resource Allocation,’’IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1941-1951, December 2018.
- B. Li, T. Chen, X. Wang and G. B. Giannakis, ‘‘Real-time Optimal Energy Management with Reduced Battery Capacity Requirements,’’ IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, to appear 2019.
Model-free interactive management for edge computing
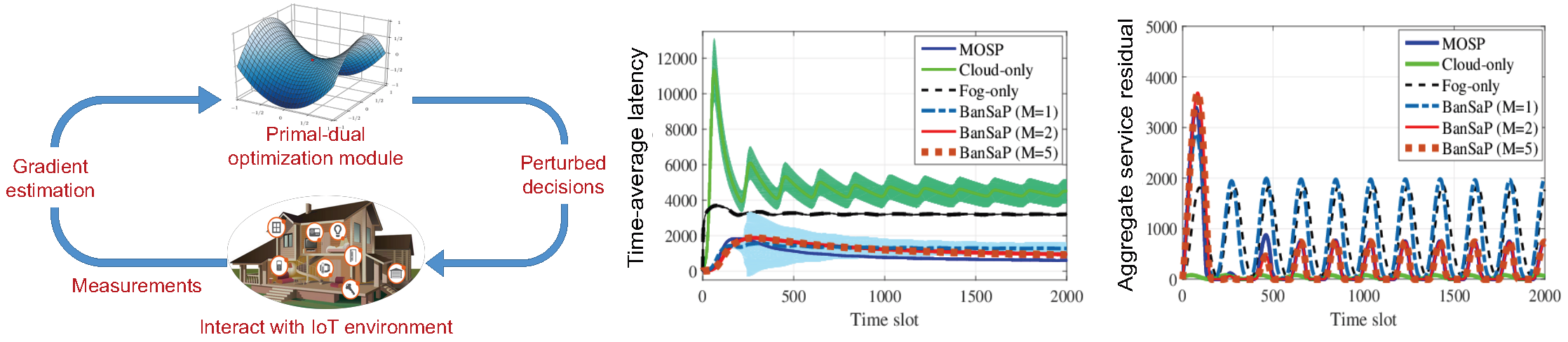
Typically, solving resource allocation problems necessitates knowledge of the models that map a resource allocation decision to its cost or utility; e.g., the model that maps transmit-power to the bit rate in communication systems. However, such models may not be available in IoT, because i) the utility function capturing e.g., service latency or reliability in edge computing, can be hard to model; and, ii) even if modeling is possible, IoT devices with limited resources may not afford the complexity of running sophisticated inference algorithms. Hence, another important ingredient of my research is to account for the feedback limited nature of resource allocation tasks in IoT. To account for physical constraints, we have considerably generalized the interactive learning tools for unconstrained problems to solve challenging constrained resource allocation problems. Tailored for edge computing scenarios, we further developed a class of model-free online learning schemes. Our new algorithms (BanSaP) come with provable performance guarantees, even when knowledge about the underlying system models can be obtained only through repeated interactions with the environment. Results in this direction were among the top 10 nominated for the best paper award in the 2017 IEEE Asilomar conference.
 |
Relevent publications:
- T. Chen, Q. Ling and G. B. Giannakis, ‘‘An Online Convex Optimization Approach to Proactive Network Resource Allocation,’’ IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 65, no. 24, pp. 6350-6364, Dec. 2017.
- T. Chen, Q. Ling, Y. Shen and G. B. Giannakis, ‘‘Heterogeneous Online Learning for Thing-Adaptive Low-Latency Fog Computing in IoT,’’ IEEE Internet of Things Journal, to appear 2018.
- T. Chen and G. B. Giannakis, ‘‘Bandit Convex Optimization for Scalable and Dynamic IoT Management,’’ IEEE Internet of Things Journal, to appear 2018.
Stochastic optimization for networked energy systems
Cyber-physical systems (CPS) are systems in which communication, computation, and control are tightly coupled and interacting with the physical world. The complexity of CPS grows when a group of task-specific systems pool their resources and capabilities together to create a networked system offering more advanced functionality. A system of systems in this type is referred to a networked CPS. In order to properly manage networked CPS, most existing approaches assume that a CPS operator can obtain perfect (future) information of CPS all times, which requires perfect computation/communication/sensing from each subsystem. Leveraging stochastic optimization toolboxes, we have tackled online resource management problems (in different forms) for data centers, smart grids, and next-generation communication systems, where the perfect information about the underlying systems is not available.
Relevent publications:
- T. Chen, X. Wang and G. B. Giannakis, ‘‘Cooling-Aware Energy and Workload Management in Data Centers via Stochastic Optimization,’’ IEEE Journal on Special Topics in Signal Processing, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 402-415, Mar. 2016.
- T. Chen, Y. Zhang X. Wang, and G. B. Giannakis, ‘‘Robust Workload and Energy Management for Sustainable Data Centers,’’ IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, Vol. 34, No. 3, pp. 651-664, Mar. 2016.
- X. Wang, X. Chen, T. Chen, L. Huang and G. B. Giannakis, ‘‘Two-scale stochastic control for integrated multipoint communication systems with renewables,’’ IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 1822 - 1834, May. 2018.